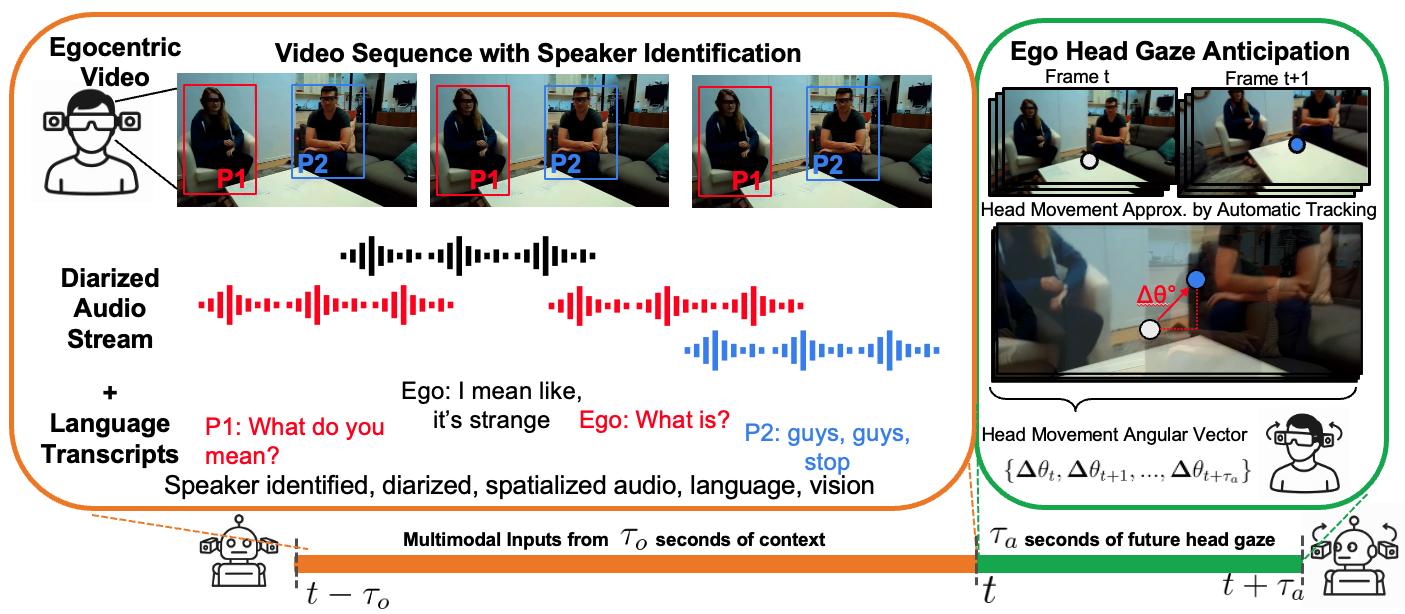
Social Egocentric Head Gaze Prediction with Vision Embeddings Fused with Speaker Audio Language
Abstract
Predicting where a person will look in a dynamic social interaction requires understanding not only visual cues, but also who is speaking, what is being said, and how conversational context unfolds over time. We present a multimodal framework for real-time egocentric head-gaze forecasting that integrates visual, audio, and language signals within a unified architecture. Our key insight is that naturally occurring egocentric human interaction videos—when combined with spatially grounded speaker cues—provide a rich supervisory signal for anticipating socially meaningful gaze behavior. To support large-scale training, we build a new 40+ hour conversation-centric egocentric benchmark drawn from Aria, Ego4D, and EgoCom, and introduce a novel method for deriving frame-level yaw–pitch gaze labels using point trajectories via video point tracking (i.e. CoTracker). This proxy supervision correlates very closely with head-mounted IMU measurements, enabling scalable annotation without specialized hardware. Our model fuses multimodal cues through a speaker-conditioned cross-attention mechanism that injects audio–language features into localized visual regions, distinguishing egocentric speech (global attention) from non-egocentric speakers (spatially localized attention) to predict short-horizon head-gaze trajectories suitable for low-latency embodied applications. Across all datasets, our approach outperforms prior state-of-the-art baselines and yields fine-grained improvements on socially relevant behaviors such as joint attention, mutual gaze, and gaze shifts. Together, these results demonstrate a scalable, multimodal pathway toward socially grounded real-time gaze anticipation for future embodied agents.
Dataset
We curate a 40+ hour conversation-centric egocentric benchmark from three prominent datasets: Aria (1.25h), Ego4D (5.9h), and EgoCom (35h). We filter for low-egomotion clips and process them into 5-second segments for training.
Proxy Head-Gaze Labels
Most casual videos lack gaze annotations. We derive proxy head-gaze labels (yaw/pitch per frame) from CoTracker point trajectories. Validated against Aria's IMU, this proxy achieves MAE 0.47° / 0.22° (yaw/pitch), enabling scalable supervision without specialized hardware.
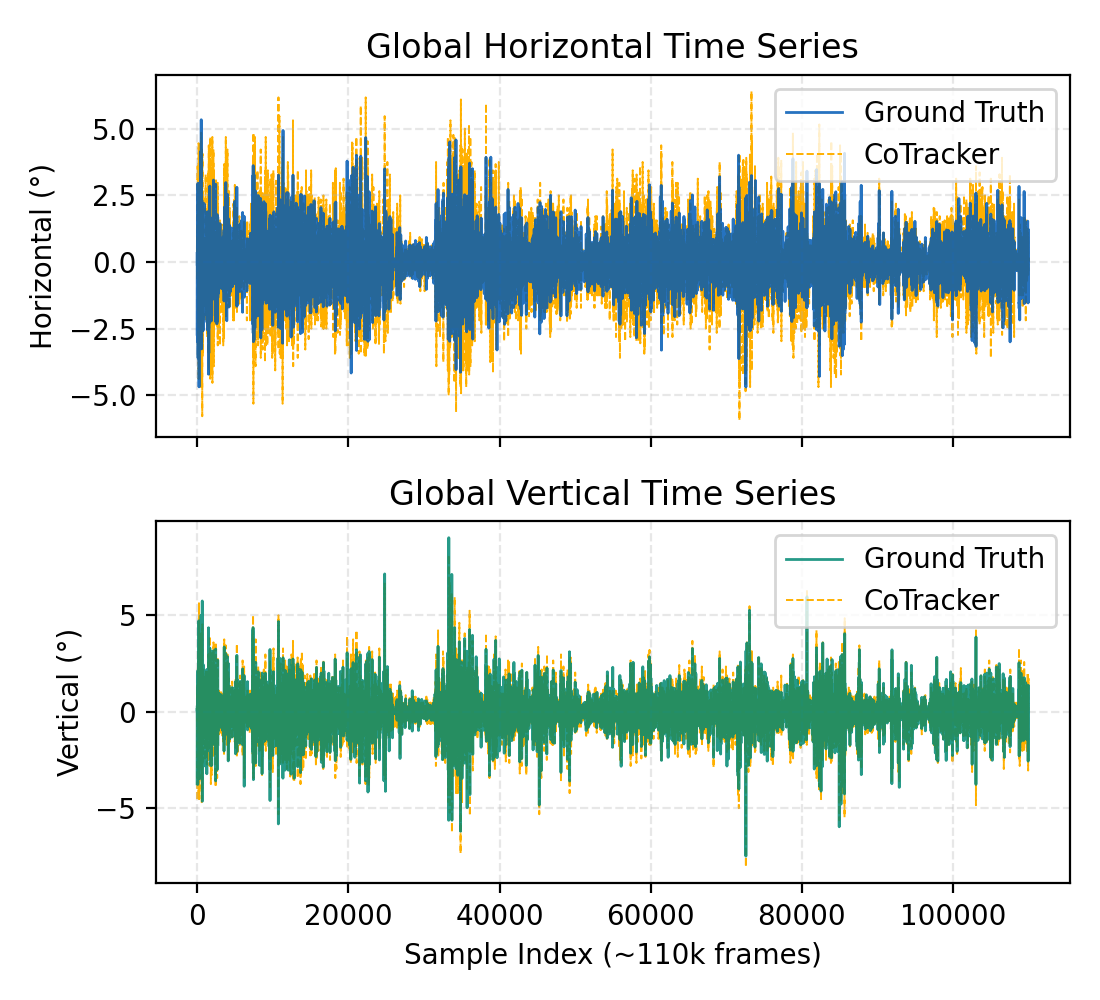
Proxy head-gaze closely tracks ground-truth IMU measurements.
Preprocessing Pipeline
Vision: Face detection (InsightFace) + body detection (YOLOv11x) with stable ID tracking across
frames.
Audio: Speaker diarization via WhisperX + pyannote to identify who is speaking when.
Methods
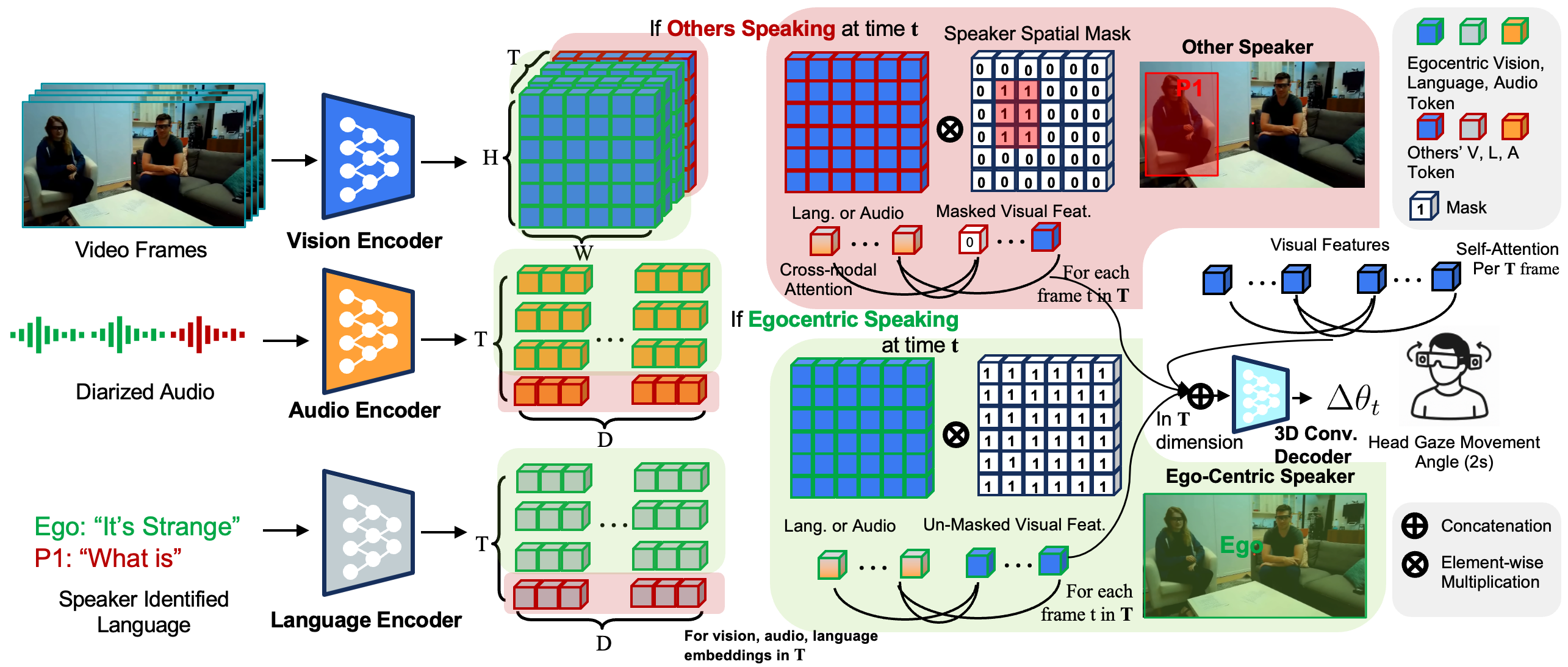
Our multimodal fusion architecture.
We fuse audio and language embeddings into the visual representation of egocentric video. Speaker-aware features are projected into the spatial regions of active speakers, creating multimodal representations that are then downsampled and decoded into gaze predictions (yaw, pitch).
Multimodal Encoders
Visual: Multi-Scale Vision Transformer (MViT) extracts spatiotemporal tokens from video.
Audio: Log-spectrogram windows processed by a transformer encoder, aligned to visual
patches.
Language: Frozen LLM encodes diarized transcripts, broadcast across spatial locations.
Speaker-Conditioned Attention
We apply masked cross-attention to inject audio-language cues into vision:
- Egocentric speech → Global attention: The wearer's voice attends to all visual patches.
- Other speakers → Localized attention: Features attend only to that speaker's spatial region.
Fused representations are passed through 3D convolutions and linear layers to predict short-horizon gaze trajectories.